
Appropriate treatments are selected depending on disease stage.
Treatment of pancreatic cancer consists of surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy and palliative care. With the rising pancreatic cancer incidence rates, the American Cancer Society estimates that 55,440 new cases will occur in the United States with 44,330 PDAC-associated deaths in 2018 ( 3).
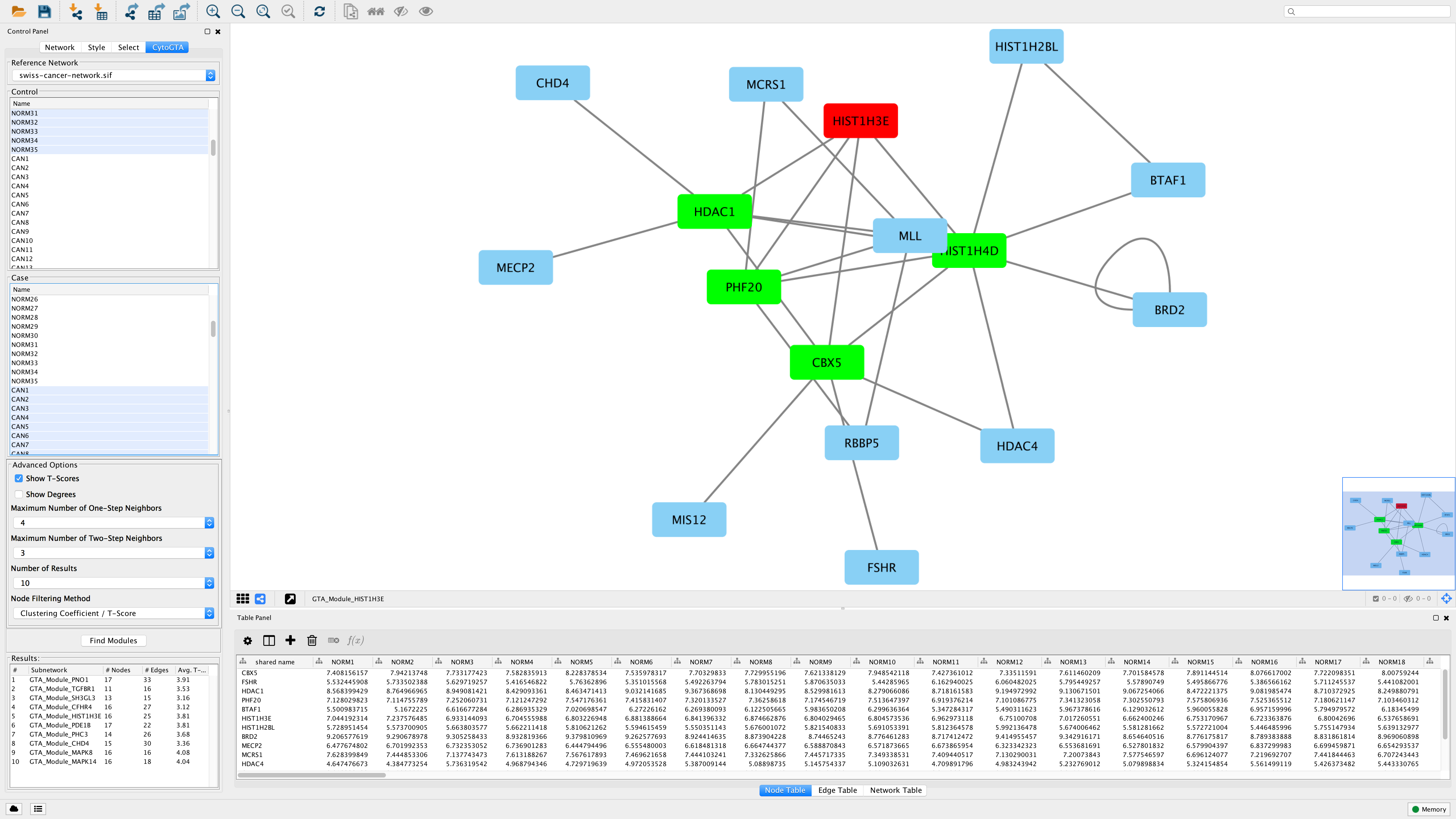
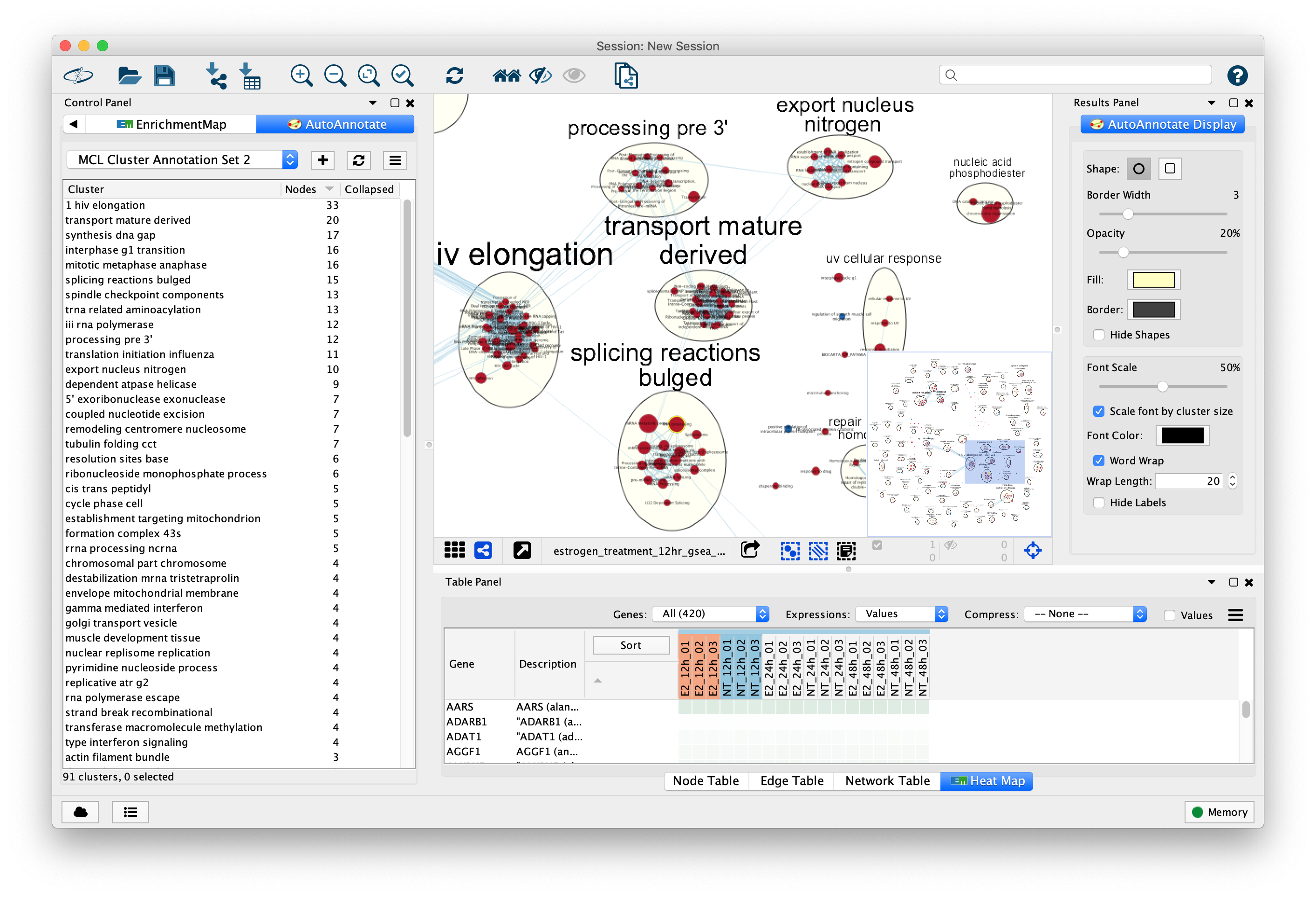
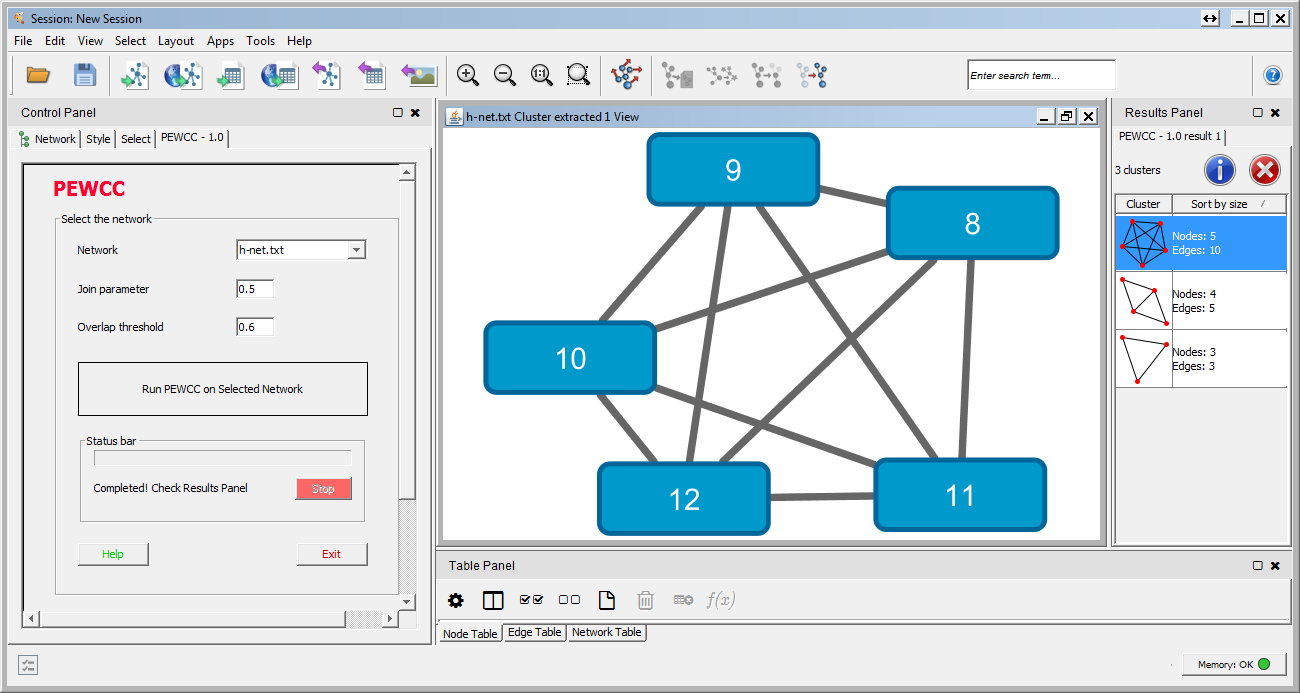
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), which accounts for ~80% of all pancreatic tumors, is an aggressive malignancy and the fourth leading cause of cancer-associated mortality worldwide ( 1, 2). The signature may serve as a potential prognostic biomarker for patients with early-stage PDAC who undergo radical resection. A prognostic signature consisting of four hub miRNAs (miR-1197, miR-218-2, miR-889 and miR-487a) associated with pathological T stage was identified to stratify the patients with early-stage PDAC into high and low risk groups. These miRNAs were predominantly involved in biological processes including ‘regulation of transcription’, ‘apoptotic process’, ‘TGF-β receptor signaling pathway’, ‘Ras protein signal transduction’ and significantly enriched in ‘cell cycle’, ‘adherens junction’, ‘FoxO’, ‘Hippo’ and ‘PI3K-Akt signaling’ pathways. The 39 hub miRNAs of the turquoise module were then detected using the ‘networkScreening’ function in R. The turquoise module containing 131 miRNAs was identified to be associated with pathological T stage (cor=−0.21 P=0.02). The expression data of 523 miRNAs in 124 patients with PDAC were analyzed in a co-expression network. A prognosis model consisting of hub miRNAs was generated using the R package ‘rbsurv’ and validated in survival analysis. Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analyses were performed on the hub miRNAs in the module of interest for functional annotation. A co-expression network was constructed to detect the modules significantly associated with clinical features by weighted gene co-expression network analysis. In the present study, miRNA expression profiles of patients with PDAC and corresponding clinical data with survival profiles were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas database. Emerging as a new class of biomarkers in human cancer, microRNAs (miRNAs/miRs) have been reported to have various tumor suppressor and oncogenic functions. Unfortunately, even following radical surgery, patient outcomes remain poor. īiological networks cluster analysis cytoscape visualization.With a 5-year survival rate of only 8%, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the fourth leading cause of cancer-associated mortality worldwide. Since it was created in July 2013, CytoCluster has been downloaded more than 9700 times in the Cytoscape App store and has already been applied to the analysis of different biological networks. CytoCluster can be easily expanded, so that more clustering algorithms and functions can be added to this plugin. In addition, BinGO is used to determine which Gene Ontology (GO) categories are statistically overrepresented in a set of genes or a subgraph of a biological network. The main function of these six clustering algorithms is to detect protein complexes or functional modules. Users can select different clustering algorithms according to their requirements. Here we present CytoCluster, a cytoscape plugin integrating six clustering algorithms, HC-PIN (Hierarchical Clustering algorithm in Protein Interaction Networks), OH-PIN (identifying Overlapping and Hierarchical modules in Protein Interaction Networks), IPCA (Identifying Protein Complex Algorithm), ClusterONE (Clustering with Overlapping Neighborhood Expansion), DCU (Detecting Complexes based on Uncertain graph model), IPC-MCE (Identifying Protein Complexes based on Maximal Complex Extension), and BinGO (the Biological networks Gene Ontology) function. Furthermore, the visualization of clustering results is crucial to display the structure of biological networks. Nowadays, cluster analysis of biological networks has become one of the most important approaches to identifying functional modules as well as predicting protein complexes and network biomarkers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
